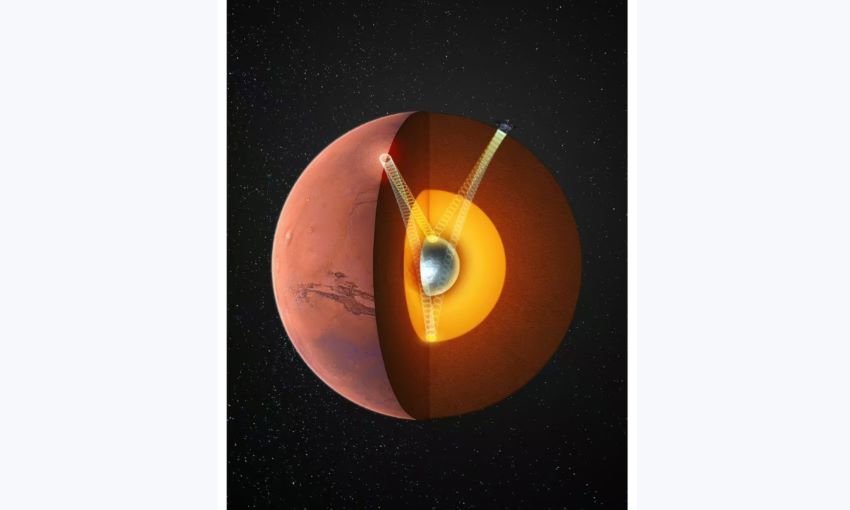
Beijing (TDI): Chinese scientists, working with international scholars, have for the first time confirmed the presence of a solid inner core in Mars with a radius of about 600 kilometers, marking a major advance in planetary science.
The findings, published in Nature on Wednesday, shed light on the Red Planet’s evolutionary history and its similarities to Earth.
The research team, led by Professors Sun Daoyuan and Mao Zhu from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), determined that Mars’ inner core is likely composed of crystalline iron-nickel alloy enriched with light elements.
Mars has long intrigued scientists as the terrestrial planet most similar to Earth. Yet, probing its interior has been challenging. While Earth’s solid core was confirmed in the 1980s, direct observational data of Mars only became available in 2018, when NASA’s InSight lander began detecting marsquakes. Since then, over a thousand events have been recorded, though weak signals and noise made deep interior studies difficult.
Read More: Pakistan Seeks to Boost Space Ties with China
By carefully analyzing seismic data, the team identified phases of waves passing through Mars’ core, revealing a layered structure: a liquid outer core surrounding a solid inner core with higher wave velocities.
The inner core accounts for about one-fifth of Mars’ radius and shows a composition that may include 12–16% sulfur, 6.7–9% oxygen, and up to 3.8% carbon. These findings help explain why Mars once had an active magnetic field but is silent today, offering crucial insights into its geologic and atmospheric evolution.
Read More: China to Train, Send Pakistani Astronauts into Space
“This is the first time a solid inner core has been confirmed in a planet beyond Earth,” said Sun. “It shows Mars also has a differentiated core-mantle structure like Earth,” according to Global Times.
The discovery highlights China’s growing role in planetary science and cross-disciplinary research. Nature reviewers praised the work, noting: “Martian seismology is notably tough, so congratulations to the authors for doing such a thorough and careful job.”